Suppose There Is a Negative Supply Shock
Suppose there is a huge spike in the demand for US currency in foreign countries. Suppose that there is a negative supply shock such as an increase in the price of imported oil.
Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com
It doesnt matter what kind of shock an economy experiences in the standard aggregate demand and aggregate supply model all long-run adjustments are made through changes in aggregate supply Blank 1 Blank 1 supply Correct Unavailable.
. Illustrate with an AS-AD diagram how the shock would affect the economy in the short-run and how the economy would adjust in the long-run. D increased transactions demand for money. The SRAS to shift to the left.
A negative supply shock. Some of them include. Negative supply shock the aggregate price level rises and aggregate output falls.
This scenario will eventually lead to A the emergence of an inflationary gap. C equilibrium real GDP to fall. The AS curve will shift upwards to the left.
Ceteris paribus in the long run a negative supply shock causes. B an increase in wages and an upward shift of the AS curve. D the price level to rise initially and then return to its lower level.
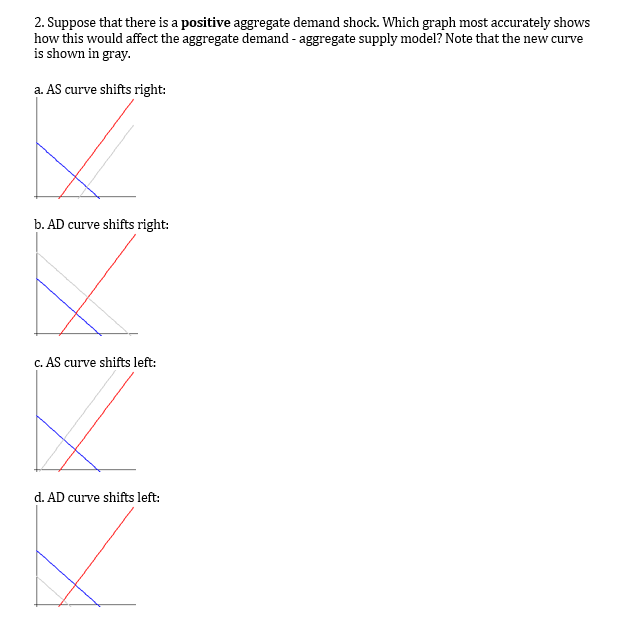
Suppose that there is a positive aggregate demand shock. This module discusses two of the most important supply shocks. Lets suppose that negative supply shock happened that affected SRAS but not LRAS.
When you have the negative supply shock your output goes down and your inflation goes up the situation known as stagflation. Starting with an economy in long-run equilibrium suppose there is now a negative supply shock eg much higher energy prices due to Middle East politics. 41 Suppose there is a recessionary gap and the Bank of Canada holds the money supply constant.
This is a negative supply shock. When there is a negative demand shock real GDP falls below the full Blank 1 Blank 1 full Correct Unavailable-employment level and. Due to negative supply shock SRAS decreased meaning that economy will be either at point B 1 real GDP supplied stayed the same but price level increased or at point B 2 price level stayed the same but real GDP.
Negative real shocks are more complicated than shocks to aggregate demand. Note that the new curve is shown in gray. In the long run we would expect.
Any increase in input cost expenses can cause the aggregate supply curve to shift to. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. As a result of this positive demand shock both the aggregate price level and aggregate output rise.
In the short run this will cause. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. Let SRAS denote the short run aggregate.
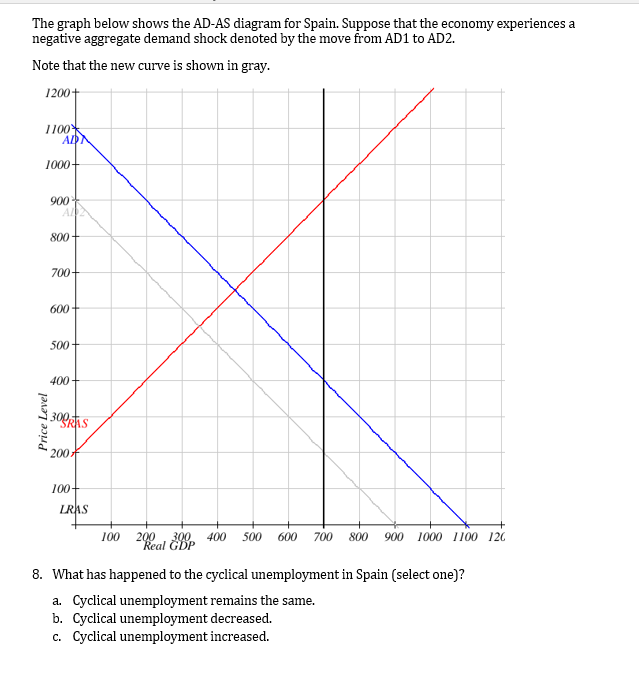
There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. AS curve shifts right. Suppose that there is a negative aggregate demand shock and the central bank commits to an inflation rate target.
The labour demand curve to shift to the right. The SRAS to shift to the right. Suppose there is a negative supply shock such as due to a flood or earthquake.
Supply curve and let AD denote the aggregate demand curve. The short-run aggregate supply curve will shift upward economic contraction will be worse. Refer to Figure 15-14.
Negative supply shocks have many potential causes. Starting with an economy in long-run equilibrium suppose there is now a negative supply shock eg much higher energy prices due to Middle East politics. Lets also assume that previously there was long-run equilibrium at point A.
Note that the new curve is. Will the economy be the same before and after the shock. An increase in the oil price implies an increase in the cost of production.
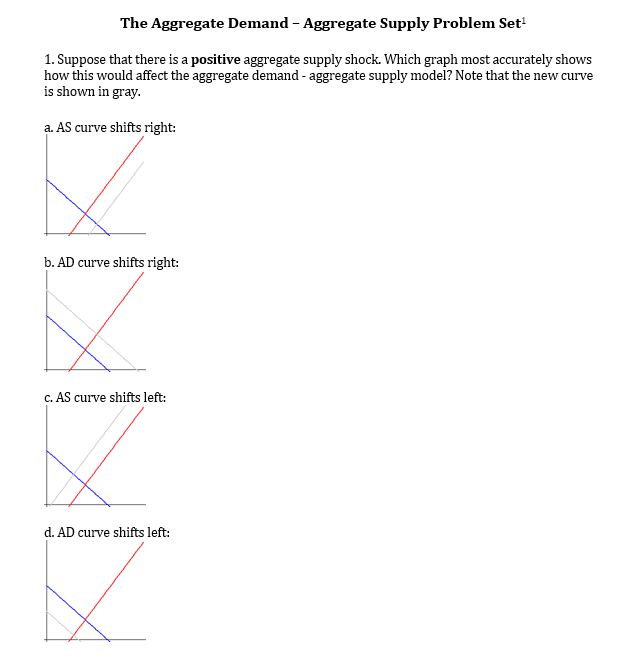
How would this affect the short-run equilibrium price and quantity. When the aggregate supply curve shifts to the right then at every price level a greater quantity of real GDP is produced. Which graph most accurately shows how this would affect aggreagte demand - aggregate supply model.
Suppose that there is a negative aggregate supply shock. The increase in real GDP to increase wages and shift the aggregate demand curve to the right. Solar energy firms launch a major program of investment spending.
A real-life example of this occurred in the 1970s. Which graph most accurately shows how this would affect the aggregate demand - aggregate supply model. That will increase the demand for US base money and other things equal will reduce the US price level.
Negative shocks or changes to aggregate supply include. This causes the equilibrium to move along the AD curve. B unemployment to fall below its short-run level.
But if the commitment is not credible then. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. Central bank rate increases.
Increased investment spending shifts the aggregate demand curve to the right. Negative not credible shift upward contraction is worse. AD curve shifts right.
A positive supply shock combined with a positive demand shock. When the AS curve shifts to the left then at every price level a lower quantity of real GDP is produced. As a result firms will be willing to supply output only at a higher price.
A positive demand shock. Assuming aggregate demand is unchanged a negative or adverse supply shock causes a products price to spike upward while a positive supply shock decreases the price. The recession of 1974-75 was caused by adverse supply shocks primarily the Oil Crisis which occurred when the Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries OPEC embargoed petroleum exports driving up the price of oil.
41 C a reduction in wages and a downward shift of the AS curve. You do not want to be an inflation nutter to the point that you would kill inflation and keep the inflation target at all costs. This is called a positive supply shock.
AS curve shifts left. A the long-run aggregate supply curve to shift to the left. Illustrate with an AS-AD diagram how the shock would affect the economy in the short-run and how the economy would adjust in.
Suppose a supply shock moves the economy from point A to point B. Suppose that there is a positive bartleby. It is a case of adverse supply shock there is a sudden and significant rise in prices.
- an increase in consumer confidence - a decrease in consumer confidence - an abrupt increase in oil prices - an increase in taxes - a decrease in taxes - a natural disaster. Solution for QUESTION 21 Suppose there is a negative supply shock and the AS curve shifts to the lef.
Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com
Solved The Aggregate Demand Aggregate Supply Problem Set1 Chegg Com

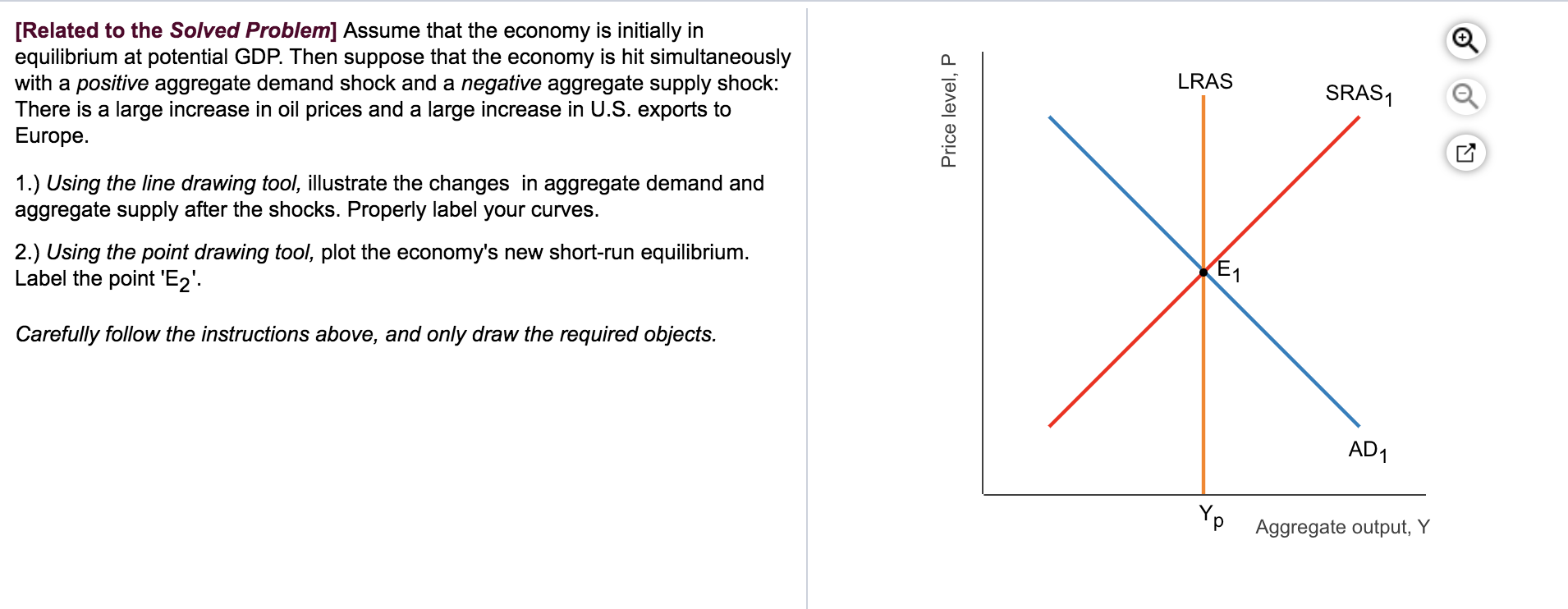
Solved Related To The Solved Problem Assume That The Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment